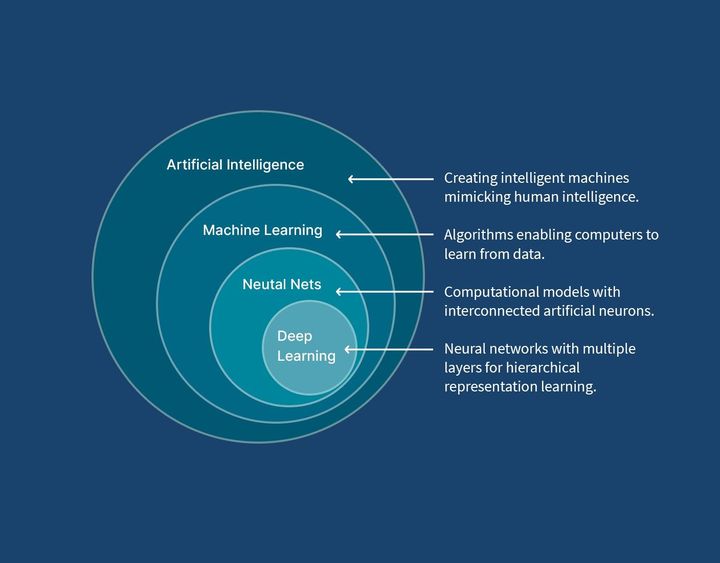
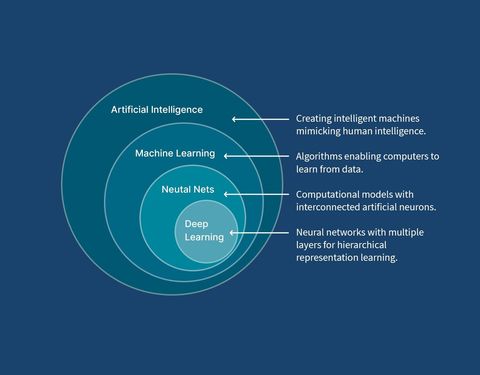
AI machine learning exists because modern societies generate massive volumes of digital data. Traditional software struggles to extract meaning from this scale and complexity. Machine learning models analyze data, identify patterns, and generate predictions or classifications that help systems adapt to new information. This approach supports smarter automation, more accurate analysis, and improved decision-making across many domains.
At a basic level, machine learning systems rely on:
-
Data as input
-
Algorithms that find patterns
-
Models that improve through training and feedback
The combination of these elements allows AI machine learning to function as a practical method for handling complex, data-driven challenges.
Importance: Why AI Machine Learning Matters Today
AI machine learning matters because it directly influences how information is processed, interpreted, and applied in modern environments. It affects individuals, organizations, and governments by improving efficiency, accuracy, and scalability.
Key reasons for its growing importance include:
-
The rapid expansion of digital data from devices, platforms, and sensors
-
The need for faster and more reliable analysis
-
Increased expectations for personalization and automation
AI machine learning helps address problems such as:
-
Managing large datasets that exceed human capacity
-
Reducing errors in repetitive or data-intensive tasks
-
Identifying trends and risks earlier through predictive analytics
People interact with machine learning daily, often without noticing it. Recommendation systems, language translation, fraud detection, and image recognition all rely on machine learning models. As these systems become more integrated into daily life, understanding their foundations becomes increasingly relevant for informed decision-making and responsible use.
Recent Updates: Trends and Developments in the Past Year
Over the past year, AI machine learning has seen notable developments focused on transparency, efficiency, and responsible use.
In early 2025, several research groups reported advances in smaller, more efficient machine learning models. These models aim to reduce computational requirements while maintaining accuracy, making AI systems more accessible across different environments.
Another key trend during 2024–2025 has been the expansion of generative AI techniques. These systems can produce text, images, and code based on learned patterns, raising new discussions about originality, reliability, and data governance.
There has also been increased attention to:
-
Explainable machine learning, which helps users understand how models reach conclusions
-
Bias detection methods to identify and reduce unfair outcomes
-
Secure model training techniques that protect sensitive data
These updates reflect a shift from rapid experimentation toward more structured, accountable adoption of AI machine learning technologies.
Laws and Policies: Regulatory Influence on AI Machine Learning
AI machine learning is increasingly shaped by laws and policy frameworks designed to encourage responsible development and use.
In the European Union, the EU Artificial Intelligence Act, formally adopted in 2024, classifies AI systems by risk level and sets requirements for transparency, data quality, and oversight. This framework has influenced global discussions on AI governance.
In India, national initiatives emphasize ethical AI and data protection through evolving digital governance programs and data protection legislation. These policies focus on safeguarding personal information while supporting innovation in AI research and deployment.
In the United States, policy guidance released between 2024 and 2025 has centered on accountability, fairness, and security, particularly for high-impact AI applications.
Across countries, common regulatory themes include:
-
Data privacy and protection
-
Transparency in automated decision-making
-
Accountability for misuse or harm
These policies aim to balance technological progress with public trust and societal well-being.
Tools and Resources: Helpful Platforms and Learning Aids
A wide range of tools and resources support understanding and working with AI machine learning concepts. These resources focus on education, experimentation, and analysis rather than commercial promotion.
Common categories include:
-
Machine learning libraries for building and testing models
-
Educational platforms offering structured learning paths
-
Visualization tools that explain model behavior and outcomes
Examples of widely referenced resources include:
-
Open-source ML frameworks for experimentation
-
Online courses and academic repositories
-
Model evaluation templates and benchmarking datasets
The table below highlights general tool categories and their purposes:
| Tool Category | Primary Purpose | Typical Users |
|---|---|---|
| ML Libraries | Model development and testing | Researchers, learners |
| Data Platforms | Dataset access and preparation | Analysts, educators |
| Visualization Tools | Interpreting model results | Students, reviewers |
These tools help users build foundational knowledge and stay aligned with current best practices in AI machine learning.
FAQs: Common Questions About AI Machine Learning
What is the difference between AI and machine learning?
AI is the broader concept of systems performing intelligent tasks, while machine learning is a method within AI that allows systems to learn from data and improve over time.
Does machine learning always require large datasets?
Not always. While many models benefit from large datasets, some techniques are designed to work with limited data using prior knowledge or transfer learning.
How accurate are machine learning models?
Accuracy depends on data quality, model design, and evaluation methods. Models are probabilistic and can make errors, which is why validation and monitoring are important.
Is AI machine learning the same as automation?
Automation uses predefined rules, while machine learning adapts based on data. Many systems combine both approaches.
Can machine learning models explain their decisions?
Some models are inherently interpretable, while others require additional techniques to explain outcomes. This area is actively developing.
Conclusion: Understanding the Role of AI Machine Learning
AI machine learning represents a foundational shift in how systems process information and support decision-making. By learning from data, these systems adapt to complexity that traditional programming cannot easily handle.
Recent developments emphasize efficiency, transparency, and ethical use, while laws and policies increasingly guide responsible adoption. Tools and educational resources continue to expand access to knowledge and experimentation.
A clear understanding of AI machine learning basics helps individuals and organizations engage with these technologies thoughtfully. As AI systems become more common, informed awareness supports better outcomes, stronger trust, and more effective use across diverse applications.