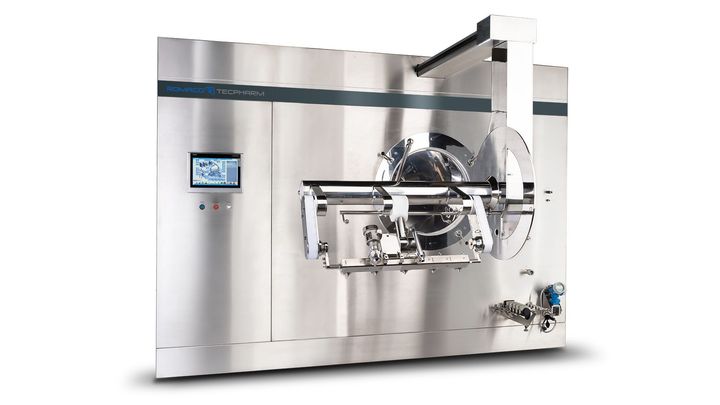
In modern pharmaceutical production, tablets are rarely left uncoated. Coating machines enable precise application of polymers, sugars, or films under controlled temperature, airflow, and spray conditions. These machines evolved from simple rotating pans to highly automated perforated drum and fluidized-bed systems that support consistent quality at industrial scale.
From a manufacturing perspective, tablet coating machines act as a bridge between formulation science and patient usability, ensuring tablets remain stable, effective, and acceptable throughout their lifecycle.
Importance: Why Tablet Coating Machines Matter Today
Tablet coating machines play a critical role in pharmaceutical quality, safety, and compliance. Their importance has grown as formulations have become more complex and regulatory expectations more stringent.
Key reasons this topic matters include:
-
Drug stability and protection: Coatings shield active ingredients from moisture, oxygen, and light.
-
Patient compliance: Taste masking and smoother surfaces make tablets easier to swallow.
-
Controlled drug delivery: Enteric and sustained-release coatings regulate where and how drugs dissolve.
-
Manufacturing efficiency: Automated systems reduce variability and batch failures.
-
Regulatory compliance: Uniform coating supports dosage accuracy and inspection requirements.
Industries affected include pharmaceutical manufacturing, nutraceutical production, and contract development organizations. Without reliable coating technology, issues such as uneven drug release, tablet breakage, or shortened shelf life can occur, leading to product recalls and compliance risks.
Recent Updates: Trends and Changes in the Past Year
Over the past year (2024–2025), tablet coating technology has seen incremental but meaningful advancements focused on efficiency, data integration, and sustainability.
Notable trends include:
-
Process Analytical Technology (PAT) adoption increased in 2024, enabling real-time monitoring of coating thickness and moisture levels.
-
Continuous coating systems gained attention in late 2024 for high-volume production environments.
-
Energy-efficient airflow designs were introduced in early 2025 to reduce heat loss and operational variability.
-
Water-based film coatings continued replacing solvent-based systems due to safety and environmental considerations.
-
Digital batch records and automation upgrades aligned coating equipment with Industry 4.0 manufacturing standards.
These updates reflect a broader shift toward smarter, data-driven pharmaceutical equipment rather than fundamental changes in coating principles.
Laws or Policies: Regulatory Framework Affecting Tablet Coating Machines
Tablet coating machines operate within strict regulatory environments because they directly influence drug quality and patient safety. Regulations vary by country but share common principles.
In the United States, oversight is guided by U.S. Food and Drug Administration requirements, particularly Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP). These rules mandate validated processes, equipment qualification, and documented control of coating parameters.
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency enforces similar GMP standards under EudraLex Volume 4, emphasizing reproducibility and contamination control.
In India, pharmaceutical coating operations fall under guidelines issued by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization, which align closely with WHO GMP standards.
Across regions, common regulatory expectations include:
-
Equipment qualification (IQ, OQ, PQ)
-
Validated coating processes
-
Cleaning and cross-contamination controls
-
Complete batch documentation and audit readiness
Tablet coating machines must therefore be designed and operated with compliance as a core requirement, not an afterthought.
Tools and Resources: Helpful References for Understanding Tablet Coating
Several tools and resources support learning, validation, and optimization of tablet coating processes.
Commonly used resources include:
-
Coating process simulators for airflow, spray rate, and drying analysis
-
GMP documentation templates for equipment qualification and validation
-
Pharmaceutical engineering handbooks covering coating theory and scale-up
-
Regulatory guidance documents from global drug authorities
-
Scientific journals focused on pharmaceutics and solid dosage forms
Below is a simplified table summarizing common tablet coating machine types and their general characteristics:
| Machine Type | Key Feature | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional Pan | Simple rotating pan | Sugar coating, small batches |
| Perforated Pan | Improved airflow | Film coating at scale |
| Fluidized Bed | Uniform particle suspension | Granule or pellet coating |
These tools and references help manufacturers and learners understand both theoretical and practical aspects of coating operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the main purpose of tablet coating?
Tablet coating protects the tablet, improves patient acceptance, and can control how the drug releases in the body.
Are all tablet coatings the same?
No. Common types include film coating, sugar coating, and enteric coating, each serving different functional needs.
Does coating change the strength of a tablet?
The coating does not change the active ingredient dose, but it can influence how quickly or where the drug dissolves.
How is coating uniformity ensured?
Uniformity is achieved through controlled rotation speed, spray rate, airflow, and validated process parameters.
Are tablet coating machines fully automated?
Many modern machines include automation and digital controls, but human oversight remains essential for compliance and quality assurance.
Conclusion
Tablet coating machines are a foundational component of modern pharmaceutical manufacturing. They exist to ensure tablets remain stable, effective, and acceptable to patients while meeting strict regulatory standards. As drug formulations evolve and compliance expectations increase, coating technology continues to adapt through improved automation, monitoring, and efficiency.
Understanding how these machines work, why they matter, and how they are regulated provides valuable insight into the broader pharmaceutical production process. While the core principles of tablet coating remain consistent, ongoing technical refinements ensure these machines remain aligned with current manufacturing and quality expectations.